Understanding Psychedelic Therapy in Clinical Trials


Exploring the Science, Process, and Potential of Psychedelic Therapy
With a focus on well-being and emotional integration, psychedelic-assisted therapy can be a transformative treatment that may help address complex mental health challenges. With proper screening, preparation, guidance, and support, psychedelic therapy shows remarkable promise as a treatment in current clinical trials.
Preliminary evidence suggests psychedelic medicines have the potential to dissolve the concepts of self and ego temporarily. This ego-dissolving effect may enable people to reframe entrenched narratives about themselves, unlocking insights and emotional breakthroughs that traditional therapies sometimes struggle to reach.
While psychedelic therapy is producing promising results, it comes with challenges and risks that require specialized training and continued scientific study. This is an introduction to psychedelic-assisted therapy: its medical indications, potential benefits, risks, and more.

What Is Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy?
The Neurobiology of Psychedelic Medicines
Classical psychedelic medicines work by interacting with the brain’s serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. When substances like psilocybin, LSD, or DMT bind to these receptors, they can induce alterations in thought processes, mood, and perception.
Non-classical psychedelics like ketamine and MDMA have other mechanisms of action involving the modulation of additional receptors. The psychedelic response produced by this action can result in a range of effects, including changes in consciousness, hallucinations, and altered sensory perceptions.
While the precise mechanisms of action are complex and not fully understood, researchers believe they involve alterations in neural connectivity, plasticity, and communication patterns within the brain. A psychedelic experience will vary from person to person, influenced by factors like dose, set and setting, and personal psychology.
Psychedelics in a Therapeutic Setting
Within a structured therapeutic framework, psychedelics may support deep introspection and emotional processing. When administered by trained professionals in a controlled setting, these compounds can help individuals gain new perspectives, enhance self-awareness, and explore personal experiences in meaningful ways.
Psychedelics such as psilocybin and LSD can intensify thoughts and emotions, making them more accessible for reflection and therapeutic processing. This heightened state may allow individuals to engage with familiar memories, patterns, or challenges from new perspectives. When past traumas or repressed emotions surface in a safe and therapeutic setting, it may present an opportunity for recognition, reflection, and emotional processing.
What Makes Psychedelics So Powerful for Healing?
Psychedelic medicines can induce profound changes in consciousness and have the potential to engender meaningful self-reflection. These compounds tap into parts of the mind that are often inaccessible, allowing patients to face and settle repressed emotions, traumatic memories, and unresolved inner conflicts.
Psychedelic medicines may enhance neural plasticity, facilitating the rewiring of neural pathways to promote healthier thought patterns and behaviors.
In psychedelic-assisted therapy, these medicines are administered by professional therapists who provide a sense of safety and guidance throughout the process as the patient prepares for, undergoes, and integrates their psychedelic experience.

The Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy Process

The Structure, Setting, and Science of Psychedelic Therapy at Sunstone Therapies
Set & Setting
“Set” and “setting” are critical to facilitating positive outcomes in psychedelic-assisted therapy.
Set refers to the mindset or mental and emotional state of the person using psychedelic medicine, while setting describes the physical and social environment in which the experience takes place.
Mindset and setting create the foundation for a safe, productive, and potentially transformative experience. Together, they set the stage for patients to explore their inner world, process emotions, and gain valuable insights for personal growth and healing.
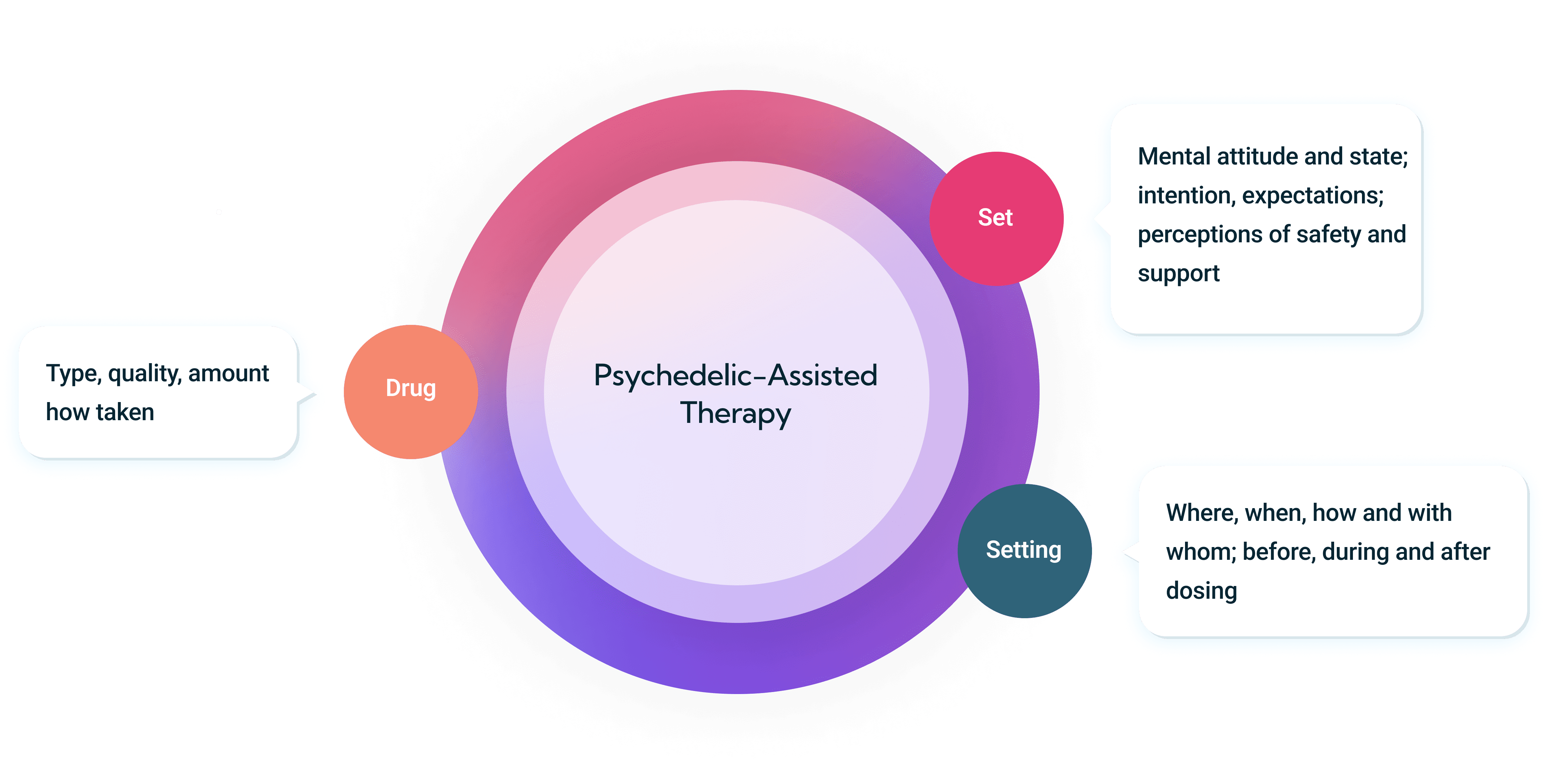
Set (Mindset)
The patient’s mindset can significantly influence their experience. Factors such as expectations, beliefs, and intentions play critical roles.

Setting (Environment)
Setting also significantly impacts the psychedelic experience. This includes physical environment, lighting, sound, and the presence of others.
A safe, comfortable, and supportive environment can help foster relaxation, security, and openness, while an uncomfortable, unfamiliar, or chaotic environment can lead to a more challenging and unsettling experience.
The aspects of setting that may contribute to positive patient outcomes include:
Physical Safety
A physically safe and comfortable environment is essential during psychedelic sessions. Every element of the space is designed to support patient well-being.
Psychological Safety
Designed for participants to feel supported, respected, and emotionally secure throughout the process.
Therapeutic Atmosphere
The physical environment plays a supportive role in the therapeutic process. Purposeful design choices—such as soft lighting, natural materials, and calming spaces—are intended to help patients feel safe, comfortable, and at ease during their participation.
The Benefits of Psychedelics
Psychedelic-assisted therapy is being explored as a potential treatment for a range of complex mental health conditions. Early research suggests that these compounds may support emotional processing, new psychological insights, and long-term symptom relief in some patients.
Psychedelic-assisted therapy is being evaluated as a potential treatment for multiple indications, including:
- Adjustment Disorder (AD)
- Alcohol Use Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Emotional Distress* in Patients with Cancer
- End-of-Life Care
- Fibromyalgia Pain Management
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD)
To explore other clinical studies, visit the National Institute of Health Clinical Trials website.

Understanding the Risks of Psychedelic Therapy
While psychedelic-assisted therapy has shown promising results in early studies, it also carries risks and contraindications (specific situations or conditions in which psychedelic therapy should not be used because it could be harmful).
Like any medical intervention, it may lead to both harm and benefit. Potential adverse effects may become more apparent as psychedelic use increases and further research is conducted. Sunstone Therapies is helping to shape protocols that minimize risk and support safety, drawing on extensive clinical experience to inform emerging standards of care.
These are some of the most common risks associated with the use of psychedelic medicines (click each dropdown to learn more):
Trauma
People with a history of severe trauma may be at risk of worsening symptoms during a psychedelic session. Psychedelics can unearth buried traumatic memories, which can be distressing and challenging to process. The guidance of an experienced therapist enables patients to navigate difficult experiences safely and constructively.
Psychological Vulnerability
People with a history of specific mental health conditions, like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, may be at higher risk of a psychotic or manic episode. In comparison, those with severe personality disorders may be at higher risk for emotional instability.
Further research is needed in these populations to determine the safety and potential benefits. For this reason, patients with these conditions or family histories have traditionally been excluded from participating in psychedelic clinical research.
Medical Conditions
Some medications can interact negatively with psychedelics. Combining certain antidepressants like SSRIs and MAOIs with psychedelics can cause a potentially fatal condition called serotonin syndrome.
Substance Abuse
Though psychedelics show promise in treating Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), people with a history of substance abuse may be at risk of using psychedelics in an unhealthy manner or experiencing cravings or relapse after a psychedelic experience. This risk is higher with certain non-classical psychedelic medicines like ketamine.
If you are considering psychedelic therapy, a thorough screening and assessment process is essential to determine your safety and suitability for the treatment.
Sunstone’s thorough assessment considers your medical history, mental health, current medications, and potential situations or conditions in which psychedelic therapy should not be used because it could cause harm. From screening to integration, the therapeutic process is conducted by trained professionals in a controlled and supportive environment, minimizing risks and ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Find answers to common patient questions
Each trial has its own set of eligibility criteria that participants must meet, such as age, medical history, and previous experiences with psychedelics. Our team will assess your eligibility during the screening process.
The primary goal of our trials is to explore the safety, effectiveness, and therapeutic potential of psychedelic medicines in a safe and supportive environment. We aim to provide participants with a healing experience while contributing to the advancement of psychedelic science.
To apply for a clinical trial, click here. We will guide you through the application and screening process.
A Research-Driven Path When
Other Treatments Haven’t Been Enough
Sunstone Therapies offers a safe, structured environment for patients exploring psychedelic-assisted therapy. Designed for those navigating complex mental health conditions, our clinical approach combines evidence-based protocols with thoughtful support. Every journey is different. We’re here for yours.
